Mathematics(2023-2024)
Series: QSS4R/4(Q.P. Code 65/4/2)
Dowload pdf :- cbse class 12 math paper 2024 set 2 series qss4r-4

Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions:
Read the following instructions very carefully and strictly follow them :
(i) This Question Paper contains 38 questions. All questions are compulsory.
(ii) Question Paper is divided into five Section- Section A, B, C, D and E.
(iii) In Section A – Question no. 1 to 18 are Multiple Choice Questions (McQs) and Question no. 19 & 20 are Assertion-Reason based questions of 1 mark each.
(iv) In Section B- Question no 21 to 25 are Very Short Answer(VSA) type questions, carrying 2 marks each.
(v) In Section (C) – Question no 26 to 31 are Short Answer (SA) type question, carrying 3 marks each.
(vi) In Section D – Question no. 32 to 35 are Long Answer (LA) type question, carrying 5 marks each.
(vii) In Section E – Question no. 36 to 38 are case study based type question, carrying 4 marks each.
(viii) There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in 2 questions in Section B, 3 question in Section C, 3 question in Section D and 2 questions in Section E.
(ix) Use of calculators is not allowed.
SECTION – A
This section consists of 20 multiple choice questions 1 mark each. 20 × 1 = 20
1. The lines ![]() and
and ![]() are perpendicular to each other for p equal to :
are perpendicular to each other for p equal to :
(A) -1/2 (B) 1/2
(C) 2 (D) 3
2. The maximum value of Z = 4x + y for a L. P. P. whose feasible region is given below is :
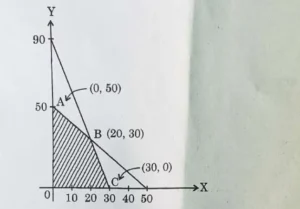
(A) 50 (B) 110
(C) 120 (D) 170
3. The probability distribution of a random variable X is :
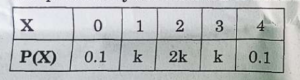
Where k is some unknown constant.
The probability that the random variable X takes the value 2 is :
(A) 1/5 (B) 2/5
(C) 4/5 (D) 1
4. If ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com A = [a_{ij}] = \begin{vmatrix} 2 & -1 & 5 \\ 1 & 3 & 2 \\ 5 & 0 & 4 \end{vmatrix}](https://gmath.in/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-55c697058b73a752af9105f36946d431_l3.png) and
and ![]() is the cofactor of element
is the cofactor of element ![]() , then the value of
, then the value of ![]() is :
is :
(A) -57 (B) 0
(C) 9 (D) 57
5. If ![]() and
and ![]() , then the value of k is :
, then the value of k is :
(A) 3 (B) 5
(C) 7 (D) 9
6. If ![]() then
then ![]() is :
is :
(A) ![]() (B) -2y/x
(B) -2y/x
(C) 2y/x (D) x/2y
7. The value of constant c that makes the function f defined by
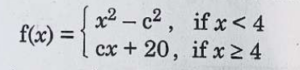
continuous for all real numbers is :
(A) -2 (B) -1
(C) 0 (D) 2
8. The value of ![]() is :
is :
(A) -2 (B) -1
(C) 1 (D) 2
9. The number of arbitrary constants in the particular solution of the differential equation
![]() ; y(0) = 0 is/are
; y(0) = 0 is/are
(A) 2 (B) 1
(C) 0 (D) 3
10. If 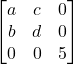 is a scalar matrix, then the value of a + 2b + 3c + 4d is :
is a scalar matrix, then the value of a + 2b + 3c + 4d is :
(A) 0 (B) 5
(C) 10 (D) 25
11. If ![]() , then the value of I – A + A² – A³ + . . . is :
, then the value of I – A + A² – A³ + . . . is :
(A) ![]()
(B) ![]()
(C) ![]()
(D) ![]()
12. Given that ![]() , matrix A is:
, matrix A is:
(A) ![]()
(B) ![]()
(C) ![]()
(D) ![]()
13. The integrating factor of the differntial equation ![]() (y > 0) is :
(y > 0) is :
(A) 1/x (B) x
(C) y (D) 1/y
14. A perpendicular to the line ![]() is :
is :
(A) ![]()
(B) ![]()
(C) ![]()
(D) ![]()
15. The vectors ![]() and
and ![]() represents the sides of
represents the sides of
(A) An equilateral triangle (B) An obtuse-angle triangle
(C) An isosceles triangle (D) A right-angle triangle
16. Let ![]() be any vector such that
be any vector such that ![]() . The value of
. The value of
![]() is :
is :
(A) a² (B) 2a²
(C) 3a² (D) 0
17. If ![]() and
and ![]() are two vectors such that
are two vectors such that ![]() and
and ![]() . then the angle between
. then the angle between ![]() and
and ![]() is :
is :
(A) π/6 (B) π/3
(C) 5π/6 (D) 11π/6
18. The function f(x) = kx – sin x is strictly increasing for
(A) k > 1 (B) k < 1
(C) k > -1 (D) k < -1
ASSERTION-REASON BASED QUESTIONS
Question No. 19 & 20 are Assertion (A) and Reason(R0 based questions carrying 1 marks each. Two statements are given, one labelled Assertion(A) and the other labelled Reason(R).
Select the correct answer from the codes (A), (B), (C) and (D) as given below :
(A) Both Assertion(A) and Reason(R) are true and the reason(R) is the correct explanation of Assertion(A).
(B) Both Assertion(A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason(R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
(C) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
19. Assertion (A): The corner points of the bounded feasible region of a L.P.P. are shown below. The maximum value Z = x + 2y occurs at infinite points.
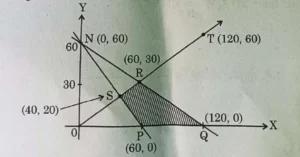
Reasons (R): The optimal solution of L.P.P. having bounded feasible region must occur at corner points.
20. Assertion (A): The relation R = [(x, y) : (x + y) is a prime number and x, y ∈ N} is not a reflexive relation.
Reason (R) : The number ‘2n’ is composite for all natural numbers n.
SECTION – B
In this section there are 5 very short answer type questions of 2 marks each.
21. The volume of a cube is increasing at the rate of 6 cm³/s. How fast is the surface area of cube increasing, when the length of an edge is 8 cm ?
22. (a) Express ![]() where
where ![]() in the simplest form.
in the simplest form.
OR
(b) Find the principal value of ![]() .
.
23. Show that ![]() is an increasing function of x in [0, π/2].
is an increasing function of x in [0, π/2].
24. (a) If ![]() , find dy/dx.
, find dy/dx.
OR
(b) If ![]() , prove that
, prove that ![]() .
.
25. Evaluate : ![]() .
.
SECTION- C
In this section there are 6 short answer type quetions of 3 marks each.
26. Given that [atex]x^y + y^x = a^b[/latex], where a and b are positive constants, find dy/dx.
27. (a) Find the particular solution of the differential equation ![]() , given that y(π/4) = 2.
, given that y(π/4) = 2.
OR
(b) Find the particular solution of the differential equation ![]() , given that y = 1 when x = 1.
, given that y = 1 when x = 1.
28. Find: ![]()
29. (a) A card from a well shuffled deck of 52 playing card is lost . From the remaining cards of the pack, a card is drawn at random and is found to be a king. Find the probability of the lost card being a King.
OR
(b) A biased die is twice as likely to show an even number as an odd number. If such a die is thrown twice, find the probability distribution of the number of sixes. Also find the mean of the distribution.
30. Solve the following L.P.P. graphically :
Maximise Z = x + 3y
subject to the constraint:
x + 2y ≤ 200
x + y ≤ 150
y ≤ 75
x, y ≥ 0
31. (a) Evaluate : ![]()
OR
(b) Find : ![]() .
.
SECTION-D
32. (a) Let A = R – {5} and B = R – {1}. Consider the fuction f : A → B, defined by ![]() . Show that f is one-one and onto.
. Show that f is one-one and onto.
OR
(b) Check whether this relation S in the set of real numbers R defined by S = {(a, b): where a – b + √2 is an irrational number} sefeiv, symmetric or transitive.
33. (a) Find the distance between e line ![]() and another line parallel to it passing through the point (4, 0, -5).
and another line parallel to it passing through the point (4, 0, -5).
OR
(b) If the lines ![]() and
and ![]() ar perpendicular to each other, find the value of k and hence write the vector equation of a line perpendicular to these two lines and passing through the point (3, -4, 7).
ar perpendicular to each other, find the value of k and hence write the vector equation of a line perpendicular to these two lines and passing through the point (3, -4, 7).
34. Use the product of matrices 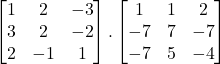 to solve the following system of equation:
to solve the following system of equation:
x + 2y 3z = 6
3x + 2y – 2z = 3
2x – y + z = 2
35. (a) Sketch the graph of y = x|x| and hence find the area bounded by this curve, X-axis and ordinates x = -2 ad = 2, using integration.
OR
(b) Using integration, find t area bounded by the ellipse 9x² + 25y² = 225, the line x = -2, x = 2 and the X-axis.
SECTION-E
In this section, there are 3 case study based question of 4 marks each.
36:- An instructor at the astronomical centre shows three among the brightest stars in a particular constellation. Assume that the telescope is located at O(0, 0, 0) and the three stars have their locations at the points D, A and V having position vectors ![]() and
and ![]() respectively.
respectively.

Based on the above information, answer the following question:
(i) How far is the star V from star A ? (1)
(ii) Find a unit vector in the direction of ![]() . (1)
. (1)
(iii)(a) Find the measure of ∠VDA . (2)
OR
(iii) (b) What is the projection of vector ![]() on vector
on vector ![]() ? (2)
? (2)
Solution: See full solution
37: Rohit Jaspreet and Alia appeared for an interview for three vacancies in the same post. The probability of Rohit’s selection is 1/5, Jaspreet’s selection is 1/3 and Alia’s selection is 1/4. The event of selection is independent of each other.
Based on the above information, answer the following question :
(i) What is the probability that at least one of them is selected ? (1)
(ii) Find ![]() where G is the event of Jaspreet’s selection and
where G is the event of Jaspreet’s selection and ![]() denotes the event that Rohit is not selected. (1)
denotes the event that Rohit is not selected. (1)
(iii) Find the probability that exactly one of them is selected. (2)
OR
(iii) (b) Find the probability that exactly two of them are selected. (2)
Solution:- See full solution
38:- A store has been selling calculators at Rs 350 each. A market survey indicates that a reduction in price (p) of calculator increases the number of units (x) sold. The relation between the price and quantity sold is given by the demand function ![]() . [CBSE 2024]
. [CBSE 2024]
Based on the above information, answer the following questions:
(i) Determine the number of units (x) that should be sold to maximise the revenue R(x) = xp(x). Also, verify result. (2)
(ii) What rebate in price of calculator should the store give to maximise the revenue ? (2)
Solution:- See full solution