Case study question of Physics – Electric charges and field
Case study 2:- Coulamb’s law states that the electrostatic force of attraction or repulsion acting between two stationary points charges is given by
![]()
Where F denotes the force between two charges ![]() and
and ![]() separated by a distance r in free space,
separated by a distance r in free space, ![]() is a constant known as permittivity of free space. Free space is vacuum and may be taken to be air practically.
is a constant known as permittivity of free space. Free space is vacuum and may be taken to be air practically.
If free space is replaced by a medium, then ![]() is repaced by
is repaced by ![]() or
or ![]() , where k is known as dielectric constant or relative permittivity.
, where k is known as dielectric constant or relative permittivity.
Read the given passage carefully and give the answer of the following questions:
Q 1:- In coulamb’s law, ![]() , then on which of the following factors does the proportionality constant k depends ?
, then on which of the following factors does the proportionality constant k depends ?
(a) Electrostatic force acting between the two charge
(b) Nature of the medium between the two charges
(c) Magnitude of the two charges
(d) Distance between the two charges
Q 2:- Dimensional formula for the permittivity constant ![]() of free space is :
of free space is :
(a) ![]() (b)
(b) ![]()
(c) ![]() (d)
(d) ![]()
Q 3:- The force of repulsion between two charges of 1 c each, kept 1 m apart in vacuum is:
(a) ![]() N
N
(b) ![]() N
N
(c) ![]() N
N
(d) ![]() N
N
Q 4:- Two identical charges repel each other with a force equal to 10 mg wt when they are 0.6 m apart in air. (g = 10 m/s²). The value of each charge is :
(a) 2 mC (b) ![]() mC
mC
(c) 2 nC (d) 2 μC
Q 5:- Coulamb’s law for the force betweenelectric charges most closely resembles with:
(a) law of conservation of energy
(b) Newton’s law of gravitation
(c) Newton’s 2 nd law of motion
(d) Law of conservation of charge
Answer :- 1. (b) Nature of the medium between the two charges.
2.(c) ![]()
As, we know that.
![]()
⇒ ![]()
⇒ ![]()
3. (b) ![]() N
N
4 (d) 2 μC
Given that, ![]() N
N
⇒ ![]()
∴ ![]()
or ![]()
Or ![]() C = 2 μC
C = 2 μC
5. (b) Newton’s law of gravitation.
Case study 1:- A charge is a property associated with the matter due to which it experiences and produces an electric and magnetic fields. Charges are scalar in nature and they add up like real numbers. Also, the total charge of an isolated system is always conserved. When the objects rub against each other, charges acquired by them must be equal and opposite.
Read the given passage carefully and give the answer of the following questions:
Q 1:- The cause of charging is:
(a) The actual transfer of protons
(b) The actual transfer of electrons
(c) The actual transfer of neutrons
(d) None of the above
Q 2:- When glass rod is rubbed with silk, then:
(a) Negative charge is produced on silk but no charge on glass rod
(b) Equal but opposite charge are produced on both
(c) Equal and similar charges are produced on both
(d) Positive charge is produced on glass rod but no charge on silk
Q 3:- If an object is positively charged theoretically, the mass of the object:
(a) Remains the same
(b) Increases slightly by a factor of ![]() kg
kg
(c) May increase or decrease
(d) Decreases slightly by a factor of ![]() kg.
kg.
Q 4:- We have two bodies with charges ![]() and
and ![]() on them, then
on them, then ![]() signify:
signify:
(a) ![]() and
and ![]() are equal charges with opposite signs
are equal charges with opposite signs
(b) ![]() and
and ![]() are equal charges with same signs
are equal charges with same signs
(c) ![]() and
and ![]() are not equal charges
are not equal charges
(d) ![]() and
and ![]() are equal charges.
are equal charges.
Q 5:- The cause of quantisation of electric charge is:
(a) Transfer of an integral number of neutrons
(b) Transfer of an integral number of protons
(c) transfer of an integral number of electrons
(d) None of the above.
Answer :- See all answer
Case study 3:- Animals emit low frequency electric fields due to a process known as osmoregulation. This process allows the concentration of ions (charged atoms or molecules) to flow between the inside of our bodies and the outside. In order for our cells to stay intact, the flow of ions needs to be balanced. But balanced doesn’t necessarily mean equal. The concentration of ions within a shrimp’s body is much lower than that of the sea water it swims in. Their voltage or potential sifference generated between the two concentrations across ‘leaky’ surfaces, can then be measured.
Read the given passage carefully and give the answer of the following questions:
Solution:- See full solution
Case study 5:- Surface charge density is defined as charge per unit surface area of surface charge distribution i.e., σ = dq/ds. Two large thin metal plates are parallel and close to each other. On their inner faces, the plates have surface charge densities of opposite sign having magnitude of ![]() C/m² as shown. The intensity of electric field at a point is
C/m² as shown. The intensity of electric field at a point is ![]() , where
, where ![]() permittivity of free space.
permittivity of free space.
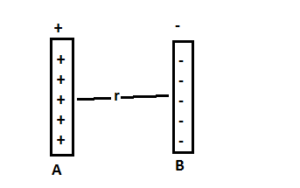
Read the given passage carefully and give the answer of the following questions:
Q 1:- What is the value of E in the outer region of the first plate ?
Solution:- See full solution