EXERCISE 4.3 (Determinants)
Question 1: Find area of the triangle with vertices at the point given in each of the following:(Class 12 ncert solution math exercise 4.3 determinants)
(i) ![]()
(ii) ![]()
(iii) ![]()
Solution: (i) The area of the triangle with vertices ![]() is given by the relation,
is given by the relation,
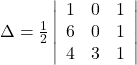
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Hence, area of the triangle is ![]() square units.
square units.
(ii) The area of the triangle with vertices ![]() is given by the relation,
is given by the relation,
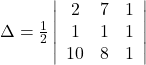
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Hence, area of the triangle is ![]() square units.
square units.
(iii) The area of the triangle with vertices ![]() is given by the relation,
is given by the relation,
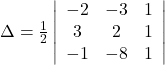
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Hence, area of the triangle is 15 square units.
Question 2: Show that the points ![]() are collinear.
are collinear.
Solution: The area of the triangle with vertices ![]() is given by the absolute value of the relation:
is given by the absolute value of the relation:
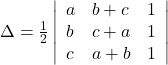
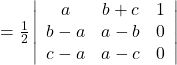
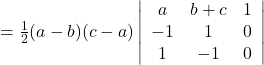
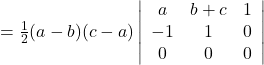
![]()
Thus, the area of the triangle formed by points is zero.
Hence, the points are collinear.
Question 3: Find values of ![]() if area of triangle is 4 square units and vertices are:
if area of triangle is 4 square units and vertices are:
(i) ![]()
(ii) ![]()
Solution: We know that the area of a triangle whose vertices are ![]() and
and ![]() is the absolute value of the determinant
is the absolute value of the determinant ![]() , where
, where
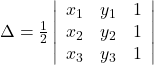
It is given that the area of triangle is 4 square units.
Hence, ![]()
(i) The area of the triangle with vertices ![]() is given by the relation,
is given by the relation,
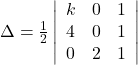
![]()
![]()
![]()
Therefore, ![]()
When ![]()
Then ![]()
When ![]()
Then ![]()
Hence, ![]()
(ii) The area of the triangle with vertices ![]() is given by the relation,
is given by the relation,

![]()
![]()
Therefore, ![]()
When ![]()
Then ![]()
When ![]()
Then ![]()
Hence, ![]()
Question 4: (i) Find equation of line joining ![]() and
and ![]() using determinants.
using determinants.
(ii) Find equation of line joining ![]() and
and ![]() using determinants.
using determinants.
Solution: (i) Let ![]() be any point on the line joining points
be any point on the line joining points ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
Then, the points ![]() and
and ![]() are collinear.
are collinear.
Hence, the area of triangle ![]() will be zero.
will be zero.
Therefore,
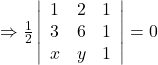
![]()
![]()
![]()
Thus, the equation of the line joining the given points is ![]() .
.
(ii) Let ![]() be any point on the line joining points
be any point on the line joining points ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
Then, the points ![]() and
and ![]() are collinear.
are collinear.
Hence, the area of triangle ![]() will be zero.
will be zero.
Therefore,
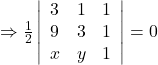
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Thus, the equation of the line joining the given points is ![]() .
.
Question 5: If area of the triangle is 35 square units with vertices ![]() . Then
. Then ![]() is
is
(A) 12
(B) ![]()
(C) ![]()
(D) ![]()
Solution: The area of the triangle with vertices ![]() is given by the relation,
is given by the relation,
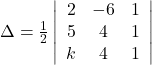
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
It is given that the area of the triangle is 35 square units
Hence, ![]() .
.
Therefore,
![]()
![]()
![]()
When, ![]()
Then, ![]()
When, ![]()
Then, ![]()
Hence, ![]()
Thus, the correct option is D.