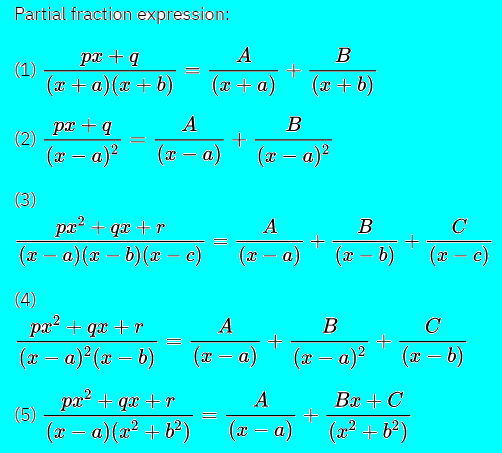
EXERCISE 7.5(Integration)
Integrate the rational functions in Exercises 1 to 21.(Ex 7.5 integration ncert maths solution class 12)
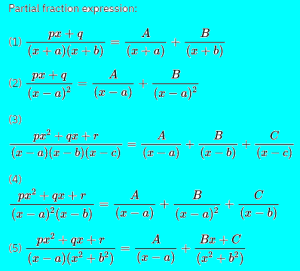
Question 1: ![]()
Solution: ![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]() putting in (i)
putting in (i)
![]()
![]()
Again putting ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Now, Integrating
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Question 2: ![]()
Solution: ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Now
![]()
Integrating
![]()
![]()
![]()
Question 3: ![]()
Solution: ![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Again Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Again let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Putting the value of A, B and C in eq (i)
![]()
Integrating
![]()
![]()
Question 4: ![]()
Solution: ![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Again Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Again let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Putting the value of A, B and C in eq (i)
![]()
Integrating
![]()
![]()
Question 5: ![]()
Solution: ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Putting in (i) and integrate
![]()
![]()
Question 6: ![]()
Solution: ![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Putting in eq (i) and integrate
![]()
![]()
![]()
Question 7: ![]()
Solution: ![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Again let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Again let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Putting in (i) and integrate
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Question 8:![]()
Solution: ![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Putting the value of A, B and C in (i) and integrate
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Question 9: ![]()
Solution: Since ![]()
![]()
![]()
Thus, ![]()
Now, ![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Putting the value of A, B and C in (i) and integrate
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Question 10: ![]()
Solution: ![]()
Thus,![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Putting the value of A, B and C and integrating
![]()
![]()
![]()
Question 11: ![]()
Solution: ![]()
Now, ![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Putting the value of A,B and C in (i) and integrate
![]()
![]()
Question 12: ![]()
Solution: ![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Putting the value of A and B in (i) and integrate
![]()
![]()
Question 13: ![]()
Solution: ![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Putting the value of A,B and C and integrate
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
Now,
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Question 14: ![]()
Solution: ![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Putting the value of A and B, and integrate
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Question 15: ![]()
Solution:Let ![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Puttinig in equation (i)
![]()
Integrating
![]()
Replacing ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Question 16: ![]()
Solution: Let ![]()
Let ![]()
Differentiate w.r.t. x
![]()
![]()
Putting in (i)
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Question 17: ![]()
Solution: Let ![]()
Let ![]()
Differentiate w.r.t. x
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Putting in (i) and integrate
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Question 18: ![]()
Solution: Let ![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Putting the value of A and B and integrate
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Question 19: ![]()
Solution: Let ![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
Using partial fraction
![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Putting in eq (i) and integrate
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Question 20: ![]()
Solution: Let ![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Adding and substracting t in numerator and denominator
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Question 21:- ![]()
Solution: Let ![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
Putting in (i)
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
Thus,
![]()
Integrating
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Choose the correct answer in each of the Exercises 22 and 23.
Question 22: ![]() equals
equals
A. 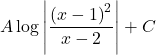
B. 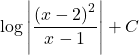
C. 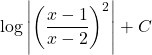
D. ![]()
Solution: The correct Answer is B.
Let ![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
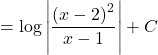
Hence, the correct Answer is B.
Question 23: ![]() equals
equals
A. ![]()
B. ![]()
C. ![]()
D. ![]()
Solution : The correct Answer is A.
Let ![]()
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Hence, the correct Answer is A.