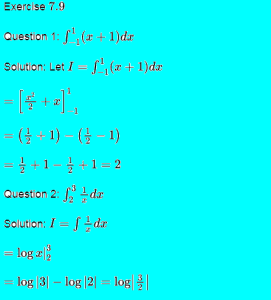Exercise 7.11
By using the properties of definite integrals, evaluate the integrals in Exercises 1 to 19.(Ex 7.11 integration ncert maths solution class 12)

Question 1: ![]()
Solution : Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
Adding (1) and (2), we have
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Question 2: ![]()
Solution: Let ![]()
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \Rightarrow I=\int_0^{\frac{\pi}{2}} \frac{\sqrt{\sin \left(\frac{\pi}{2}-x\right)}}{\sqrt{\sin \left(\frac{\pi}{2}-x\right)}+\sqrt{\cos \left(\frac{\pi}{2}-x\right)}} d x \quad\left[\text { Using property: } \int_0^a f(x) d x=\int_0^a f(a-x) d x\right]](https://gmath.in/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-4c26c2f671d70014e6bf80e9a78800de_l3.png)
![]()
Adding (1) and (2), we have
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Question 3: ![]()
Solution:Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
Adding (1) and (2), we have
![]()
![]()
Question4: ![]()
Solution: Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Question 5: ![]()
Solution: Let ![]()
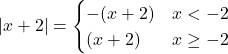
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Question 6: ![]()
Solution: Let ![]()
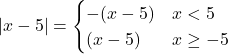
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Question 7: ![]()
Solution: Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Question 8: ![]()
Solution: Let ![]()
![]()
![]() Using property:
Using property: ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Question 9: ![]()
Soltuion: Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Question 10: ![]()
Solution: Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Using property, ![]() , we have
, we have
![]()
Adding (1) and (2), we have
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Question 11: ![]()
Solution: Let ![]()
Here, ![]() , therefore,
, therefore, ![]() is an even function.
is an even function.
We know that if ![]() is an even function, then
is an even function, then ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Question 12: ![]()
Solution:- Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Question 13: ![]()
Solution: Let ![]()
Here, ![]() , therefore,
, therefore, ![]() is an odd function.
is an odd function.
We know that if ![]() is an even function, then
is an even function, then ![]()
Therefore, ![]()
Question 14: ![]()
Solution: Let ![]()
We know that,
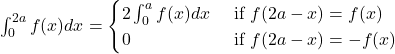
Here, ![]()
![]()
Now, ![]()
![]()
Question 15: ![]()
Solution : Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Adding (1) and (2), we have
![]()
![]()
Question 16: ![]()
Solution : Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Adding (1) and (2), we have
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
We know that,
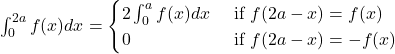
Here, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Adding (4) and (5), we have
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
Question 17: ![]()
Solution : Let ![]()
![]() Using property:
Using property: ![]() , we have
, we have
![]()
Adding (1) and (2), we have
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Question 18: ![]()
Solution : ![]()
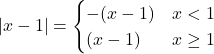
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Question 19: Show that ![]() if
if ![]() and
and ![]() are defined as
are defined as ![]() and
and ![]()
Solution : Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Adding (1) and (2), we have
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Question 20: The value of ![]() is
is
(A) 0
(B) 2
(C) ![]()
(D) 1
Solution : The correct answer is (C)
Let ![]()
![]()
We know that,
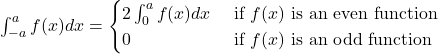
Therefore,
![]()
![]()
Hence, the correct answer is (C).
Question 21: The value of ![]() is
is
(A) 2
(B) ![]()
(C) 0
(D) ![]()
Solution: The correct answer is (C)
Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Hence, the correct answer is (C).