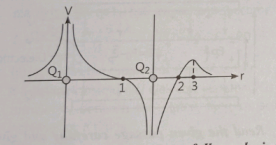
Case study 1:- The potential at any observation point P of a static electric field is defined as the work done by the external agent (or negative of work done by electrostatic field) in slowly bringing a unit positive point charge from infinity to the observation point. Figure shows the potential variation along the line of charges. Two point charges ![]() and
and ![]() lie along a line at a distance from each other.
lie along a line at a distance from each other.
Read the given passage carefully and give the answer of the following questions:
Q 1. At which of the points 1, 2 and 3 is the electric field zero ?
(a) 1 (b) 2
(c) 3 (d) Both a. and b.
Q 2:- The signs of charges ![]() and
and ![]() respectively are :
respectively are :
(a) Positive and negative
(b) Negative and Positive
(c) Positive and positive
(d) Negative and negative
Q 3:- Which of the two charges ![]() and
and ![]() is greater in magnitude ?
is greater in magnitude ?
(a) ![]()
(b) ![]()
(c) Same
(d) Can’t be determined
Q 4:- Which of the following statement is not true ?
(a) Electrostatic force is a conservative force.
(b) Potential energy of charge q at a point is the work done per unit charge in bringing a charge from any point to infinity.
(c) When two like charges lie infinite distance apart. Their potential energy is zero.
(d) Both a, and c.
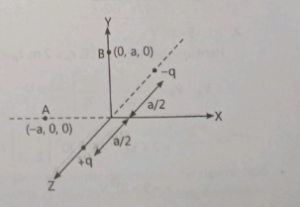
Q 5:- Positive and negative charges of equal magnitude are kept at (0, 0, a/2) and (0, 0, -a/2) respectively. The work done by the electric field when another positive point charge is moved from (-a, 0, 0) to (0, a, 0), is:
(a) Positive
(b) Negative
(c) zero
(d) Depends on the path connecting the initial and final positions.
Answer:- 1. (c) 3
As ![]() , the negative of the slope of V versus r curve represents the components of electric field along r. Slope of curve is zero only at point 3.
, the negative of the slope of V versus r curve represents the components of electric field along r. Slope of curve is zero only at point 3.
Therefore, the electric field vetor is zero at point 3.
2. (a) Positive and negative
Near positive charge, net potential is positive and near a negative charge, net potential is negative.Thus, charge ![]() is positve and
is positve and ![]() is negative.
is negative.
3. (b) ![]()
From the figure, it can be seen that net potential due to two charges is positive everywhere in the region left to charge ![]() . Therefore, the magnitude of potential due to charge
. Therefore, the magnitude of potential due to charge ![]() is greater than due to
is greater than due to ![]() .
.
4. (b) Potential energy of charge q at a point is the work done per unit charge in bringing q charge from any point to infinity.
5. (c) Zero
It can be seen that potential at the points both A and B are zero. When the charge is moved from A to b. Work done by the electric field on the charge will be zero.
Case study 4:- Potential difference (ΔV) between two points A and B separated by a distance x in a uniform electric field E is given by ΔV = -Ex, where, x is measured parallel to the field lines. If a charge ![]() moves from P to Q, the changes in potential energy (ΔU) is given as ΔU =
moves from P to Q, the changes in potential energy (ΔU) is given as ΔU = ![]() . A proton is released from rest in uniform electric field of magnitude
. A proton is released from rest in uniform electric field of magnitude ![]() directly along the positive X-axis. The proton undergoes a displacement of 0.25 m in the direction of E.
directly along the positive X-axis. The proton undergoes a displacement of 0.25 m in the direction of E.
Mass of a proton ![]() kg and charge of proton
kg and charge of proton ![]() C
C
Read the given passage carefully and give the answer the following questions:
Q 1:- What will be the change in electric potential of the proton between the points A and B ?
Solution:- See full solution