Question 3:- Solve the differential equation ![]() ; given y(1) = 2. [CBSE 2025]
; given y(1) = 2. [CBSE 2025]
Solution:- Given, ![]()
⇒ ![]()
⇒ ![]()
⇒ ![]()
Integrate both side
⇒ ![]()
⇒ ![]()
⇒ ![]()
⇒ ![]() . . . (i)
. . . (i)
Given y(1) = 2
![]()
⇒ ![]()
⇒ ![]()
Hence, from equation (i)
![]()
⇒ ![]()
⇒ ![]()
⇒ ![]()
⇒ ![]()
⇒ ![]()
Question 1:- Using integration, find the area of the region bounded by the line y = 5x + 2, the x- axis and the ordinates x = -2 and x = 2. [CBSE 2025]
Solution:- See full solution
Question 2:- Solve the following differential equation :
![]() .
.
Solution:- See full solution
Question 4:- Find the image A‘ of the point A (2, 1, 2) in the line l : ![]() . Also, find the equation of the line joining AA’. Find the foot of perpendicular from point A on the line l.
. Also, find the equation of the line joining AA’. Find the foot of perpendicular from point A on the line l.
Solution:- See full solution
Question 5:- Find the shortest distance between the lines :
![]()
![]() .
.
Solution:- See full solution
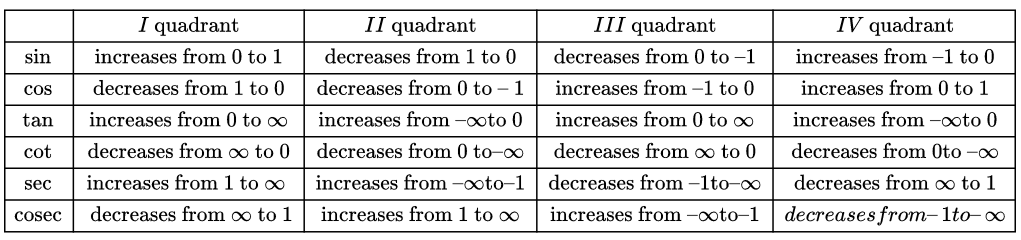
Trigonometry Formulae class 11