Question 5:- Find the shortest distance between the lines :
![]()
![]() .
.
Solution:- Shortest distance between two skew line
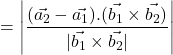
Point on Ist line = (-1, 1, 9) and dr’s of Ist line = (2, 1, -3)
Point on IInd line = (3, -15, 9) and dr’s of IInd line = (2, -7, 5)
Since, ![]()
![]()
![]()
⇒ ![]()
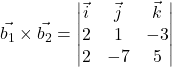
⇒ ![]()
⇒ ![]()
![]()
⇒ ![]()
![]()
⇒ ![]()
Shortest distance between two skew line
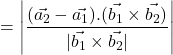
![]()
![]()
![]()
Question 1:- Using integration, find the area of the region bounded by the line y = 5x + 2, the x- axis and the ordinates x = -2 and x = 2. [CBSE 2025]
Solution:- See full solution
Question 2:- Solve the following differential equation :
![]() .
.
Solution:- See full solution
Question 3:- Solve the differential equation ![]() ; given y(1) = 2.
; given y(1) = 2.
Solution:- See full solution
Question 4:- Find the image A‘ of the point A (2, 1, 2) in the line l : ![]() . Also, find the equation of the line joining AA’. Find the foot of perpendicular from point A on the line l.
. Also, find the equation of the line joining AA’. Find the foot of perpendicular from point A on the line l.
Solution:- See full solution
Question 6:- A die with number 1 to 6 is biased such that P(2) = 3/10 and probability of other numbers is equal. Find the mean of the number of times number 2 appears on the dice, if the dice is thrown twice.
Solution:- See full solution
Question 7:- If y = log(√x + 1/√x)², then show that ![]() .
.
Solution:- See full solution
Question 8:- Two dice are thrown Defined are the following two events A and B : A = {(x, y): x + y = 9}, B = {(x, y) : x ≠ 3}, Where (x, y) denote a point in the same sample space.
Check if events A and B are independent or mutually exclusive.
Solution:- See full solution